Women in Manufacturing
Women in Manufacturing
Women make up nearly one-third of the manufacturing industry workforce in the United States. Women play a number of roles in manufacturing from working on the production line to running their own manufacturing businesses. Today we explore the role of women in the manufacturing industry using household data from the American Community Survey. Industry refers to the kind of business conducted by a person’s employment organization; occupation describes the kind of work that a person does on the job.
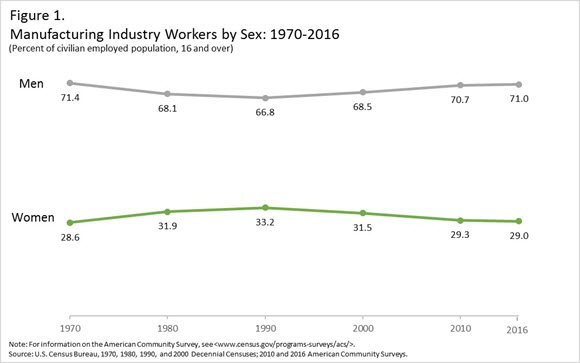
Although women make up nearly half of the working population (47.5 percent), they remain underrepresented in the manufacturing industry. Historically, men have held the majority of jobs in the manufacturing industry. Figure 1 shows that since 1970, women’s share of employment in the manufacturing industry has remained relatively constant, peaking at 33.2 percent in 1990 before declining to 29.0 percent in 2016.
In 2016, 60.0 percent of women working in the manufacturing industry were white, compared with 18.7 percent Hispanic and 11.3 percent black. Median earnings for female manufacturing industry workers was higher ($35,158) than that of women in all industries ($30,348) yet lower than that for male manufacturing workers ($48,849).
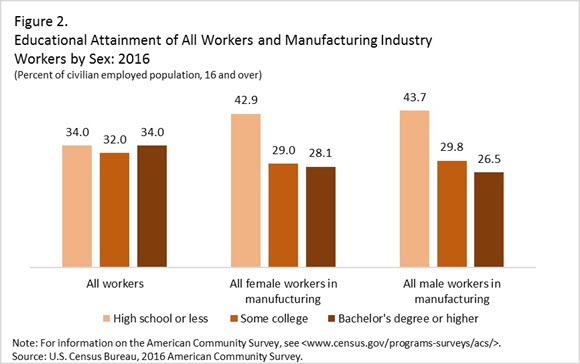
Compared with all workers, female manufacturing workers are less likely to have a bachelor’s degree or higher (see Figure 2). Just over four in 10 (42.9) women working in the manufacturing industry had a high school diploma or less, compared with 34.0 percent of all workers. Female and male manufacturing workers had comparable rates of education below the college level. However, a higher percentage of women working in manufacturing had a bachelor’s degree or higher (28.1 percent and 26.5 percent, respectively).
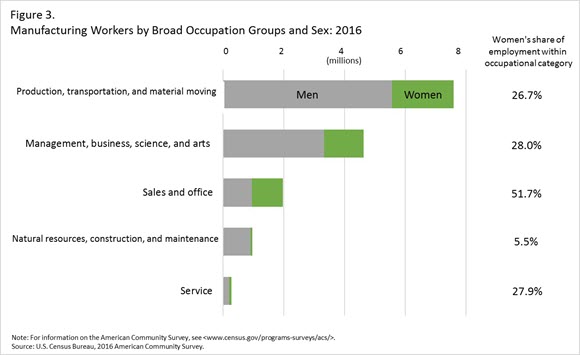
Analyzing occupations provides further insight into where women are working within the manufacturing industry. A wide range of skilled, professional or semi-skilled employees contributed to the manufacturing industry. Around 7.6 million production, transportation, and material moving workers were employed in the manufacturing industry in 2016 (Figure 3). While production, transportation, and material moving occupations employed the largest number of women within the manufacturing industry, women only made up about one-quarter (26.7 percent) of these workers. The most common detailed production occupations with over 100,000 female workers within the manufacturing industry include miscellaneous assemblers and fabricators; production workers, all other; and inspectors, testers, sorters, samplers, and weighers.
Women comprise a larger share of workers in sales and office occupations within the manufacturing industry (51.7 percent). Within this broad occupation group, occupations with over 100,000 female workers included secretaries and administrative assistants; sales representatives, wholesale and manufacturing; and customer service representatives.
What does the future of manufacturing hold for women? Advances in technology have changed the way that goods are produced. Many manufacturing jobs of the future will require highly specialized skills. Pursing a Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) education may help prepare the future generation of manufacturing workers. Although women, especially younger women, have gained relative to their male counterparts in college completion, they are less likely to earn degrees related to STEM. Increasing the number of women who receive STEM related college degrees may help prepare women for careers in the manufacturing industries.
To view these statistics along with other social and demographic statistics for women workers, visit: