Census Bureau’s 2023 Annual Business Survey Provides Insight into Technology Adoption by Businesses
The adoption of new technology like robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) had little impact on the number or skills of workers that businesses employ, according to the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2023 Annual Business Survey (ABS).
The ABS surveys employer businesses (those with at least one paid employee) on many aspects of business ownership including why and when they became owners, how they manage their finances and how technology impacts their workforce.
All In On AI?
Contrary to conventional wisdom, the 2023 ABS (which produced 2022 data) found that adoption of technology, including AI, did not change overall worker numbers.
Businesses most often reported their “number of workers did not change overall” between 2020 and 2022 after adopting any of the five technologies the ABS tracked: AI, specialized software, robotics, cloud-based tech or specialized equipment.
About 78% of organizations reported using AI in 2024, up from 55% the year prior, according to Stanford’s 2025 AI Index. Recent analyses found that AI has had — at least so far — little impact on employment numbers.
Some jobs, like financial examiner, are more “exposed” to AI than, say, a construction worker whose job can’t be easily simulated by an AI model. But research from the Economic Innovation Group shows that from 2022 to the beginning of 2025, the unemployment rate rose less for the most AI exposed workers (up 0.30 percentage points) than for the least AI-exposed workers (up 0.94 points).
Impact of Technology on Workers
Businesses most often reported their “number of workers did not change overall” between 2020 and 2022 after adopting any of the five technologies the ABS tracked: AI, specialized software, robotics, cloud-based tech or specialized equipment (Figure 1).
When these technologies did have an impact, all (except robotics) were reportedly more likely to increase than decrease worker numbers.
There was no statistically significant difference between the number of workers increased (9.5%) or decreased (8.1%) by robotics.
When compared, none of the technologies significantly increased worker numbers more than any other.
Impact of Technology on Worker Skills
Most businesses also reported these technologies had little or no impact on worker skill level (Figure 2).
AI was the technology businesses most often cited as positively affecting the skill level of workers (Figure 2).
Only 3.9% of businesses using robotics and 3.3% of businesses using AI reported workers’ skill level decreased — the largest shares in this category (with no statistically significant difference between them).
AI (40.7%), specialized equipment (50.2%) and robotics (56.6%) largely had no overall impact on worker’s scientific, technological, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) skills (Figure 3).
When a technology did alter skills of STEM workers, it was more likely to boost than diminish them — with robotics (20.7%) and AI (22.1%) the most likely.
Cloud-based technology and specialized software were most often found “not applicable” to STEM worker skills (40.9% and 41.6%, respectively) or to have caused no change overall (44.4% and 44.9%, respectively). There were no statistically significant differences between these two impact categories and technologies.
Why Companies Embrace New Technologies
Improving the quality or reliability of processes or methods was the most common motivating factor for businesses to adopt cloud-based technology (51.8%), specialized software (49.8%) and AI (45.8%) between 2020 and 2022 (Figure 4).
Specialized equipment and robotics were the only categories in which improving processes or methods was not the top motivating factor.
The top reason cited for adopting specialized equipment was to improve the quality or reliability of goods or services (49.8%).
Businesses used robotics to automate tasks performed by human labor (50.8%), improve the quality or reliability of goods and services (41.8%), and improve the quality or reliability of processes or methods (43.6%). The differences between these motivations were not statistically significant.
When Technology was Adopted
Businesses used AI at a higher rate (68.0%) than other technologies from 2021 to 2022.
But they adopted other surveyed technologies at a higher rate from 2016 to 2020:
- Cloud-based (40.0%).
- Specialized software (27.0%).
- Specialized equipment (23.6%).
Adoption of robotics technology remained relatively steady, ranging from 23.6% to 26.9% between 2016 and 2022 (with no significant difference between these shares).
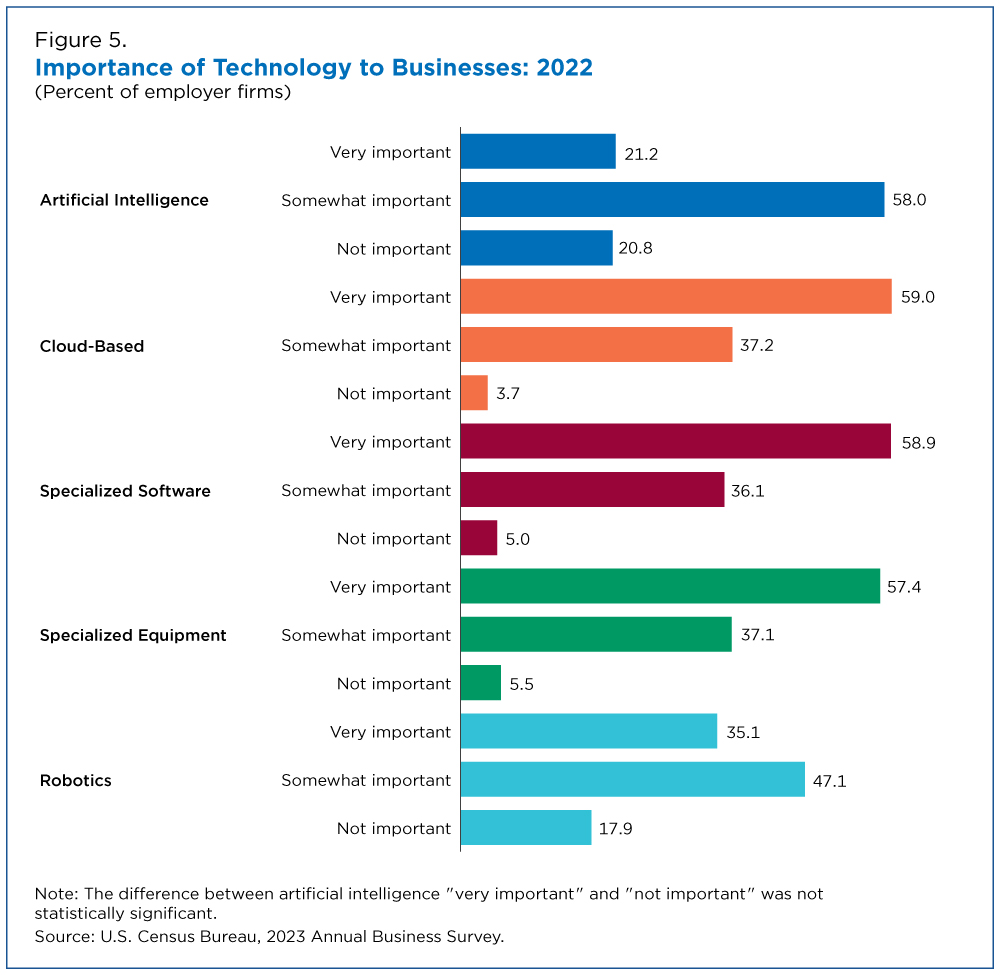
The Importance and Impact of Technology
Most businesses reported cloud-based technology (59.0%), specialized software (58.9%), and specialized equipment (57.4%) were “very important” to their processes or methods (Figure 5).
In contrast, they said robotics (47.1%) and AI (58.0%) were only “somewhat important.”
Overall, respondents pointed to cloud-based and specialized software as the two most important technologies for improving business processes and methods.
Information about confidentiality and sampling and nonsampling error for the 2023 ABS are available on the ABS Methodology page.
Related Statistics
Subscribe
Our email newsletter is sent out on the day we publish a story. Get an alert directly in your inbox to read, share and blog about our newest stories.
Contact our Public Information Office for media inquiries or interviews.
-
Business and EconomyHow Many U.S. Businesses Use Artificial Intelligence?November 28, 2023The Business Trends and Outlook Survey shows that only 3.8% of businesses use AI to produce goods and services but use varies by sector.
-
EmploymentWhere in the United States Are the High-Tech Jobs?February 14, 2023Census Bureau’s new Business Dynamics Statistics of U.S. High Tech Industries shows where high-tech jobs are and where new high-tech companies are locating.
-
Business and EconomyExploring Two “First Look” Economic DatasetsJune 06, 2024Early data from the 2022 Economic Census and 2023 Annual Business Survey offer a glimpse of the number of employer businesses in the United States.
-
EmploymentUnexpected Workforce Trends in Post-Pandemic ManhattanFebruary 19, 2026Recent jobs data show Manhattan’s workforce shares have shifted younger, more female and into the Accommodation and Food Services industries after the pandemic.
-
Business and EconomyAbility to Borrow Money Offers Clues to Financial Health of BusinessesFebruary 10, 2026Most employer businesses that applied for credit got what they asked for, according to the latest available data from the Annual Business Survey.
-
IncomeHow Income Varies by Race and GeographyJanuary 29, 2026Median income of non-Hispanic White households declined in five states over the past 15 years: Alaska, Connecticut, Louisiana, Nevada, and New Mexico.
-
HousingRental Costs Up, Mortgages Stayed FlatJanuary 29, 2026Newly Released American Community Survey compares 2020-2024 and 2015-2019 housing costs by county.