Declines in Medicaid Coverage Rates in 30 States Drove Up State Uninsured Rates From 2023 to 2024
The uninsured rate increased in 18 states and the District of Columbia between 2023 and 2024, according to a brief on the 2024 American Community Survey (ACS) 1-year estimates released today.
What is contributing to the increase?
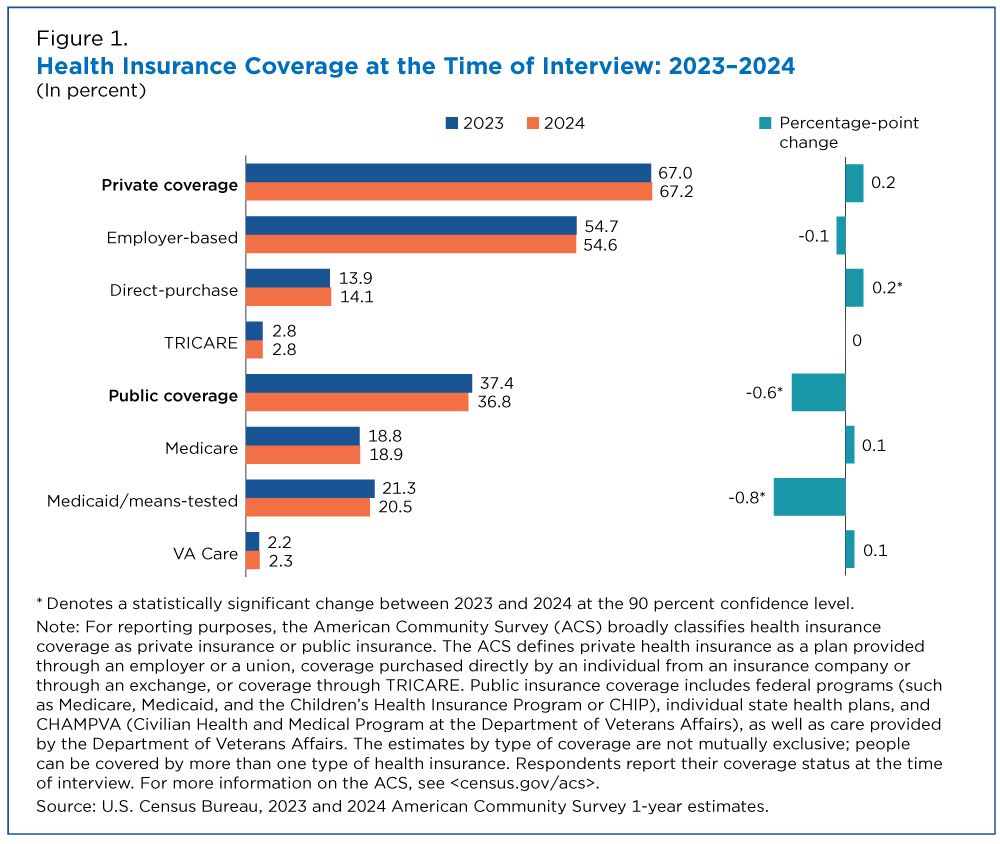
A drop in public health coverage, most notably Medicaid, according to data from the 2024 ACS that reports health insurance coverage at the time the survey is taken.
Medicaid coverage rates dropped in 22 states for children under 19 and in 33 states for those ages 19 to 64.
The percentage of ACS respondents who reported having public health insurance (when interviewed) declined from 37.4% in 2023 to 36.8% in 2024 (Figure 1). The reduction in public coverage was concentrated in Medicaid, which declined from 21.3% to 20.5% (Table 1).
End of Pandemic-Related Health Provisions
Some of the drops in Medicaid coverage rates were partially due to expiration of COVID-19 pandemic-related public health provisions.
The COVID-19 pandemic spurred passage of the Families First Coronavirus Response Act, which mandated that states maintain continuous enrollment for individuals enrolled in Medicaid on or after March 8, 2020.
As of February 2023, states were no longer required to maintain continuous Medicaid enrollment and were expected to resume regular eligibility determinations within 14 months, ending enrollment for some recipients.
These changes likely contributed to decreased Medicaid coverage and higher uninsured rates between 2023 and 2024.
Percentage of People with Medicaid Declined in Most States
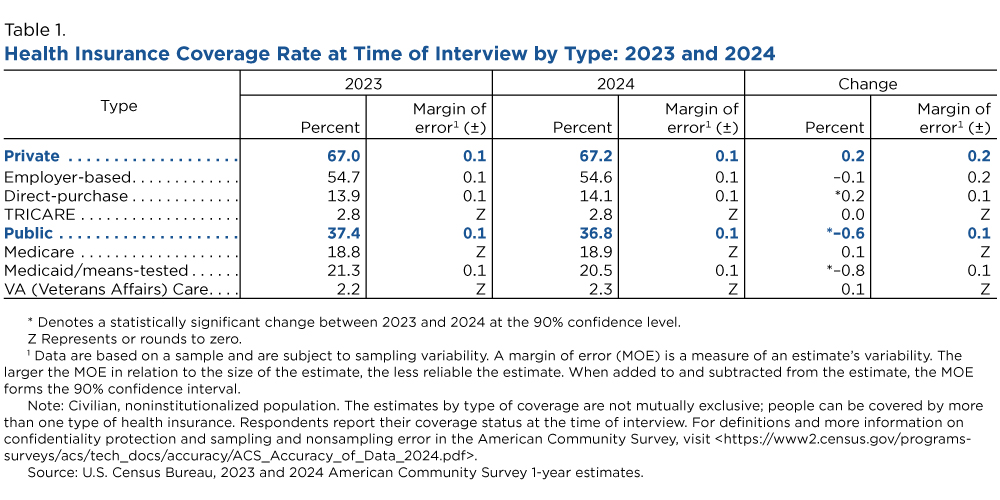
In 2024, the percentage of people covered by Medicaid declined in 30 states. Only two states — California and North Carolina — reported increased Medicaid coverage, reflecting additional state program expansions (Figure 2).
Medicaid coverage rates dropped in 22 states for children under 19 and in 33 states for those ages 19 to 64.
This analysis focuses on the under-65 population since in most states changes in Medicaid coverage rates were not statistically significant among those 65 and older.
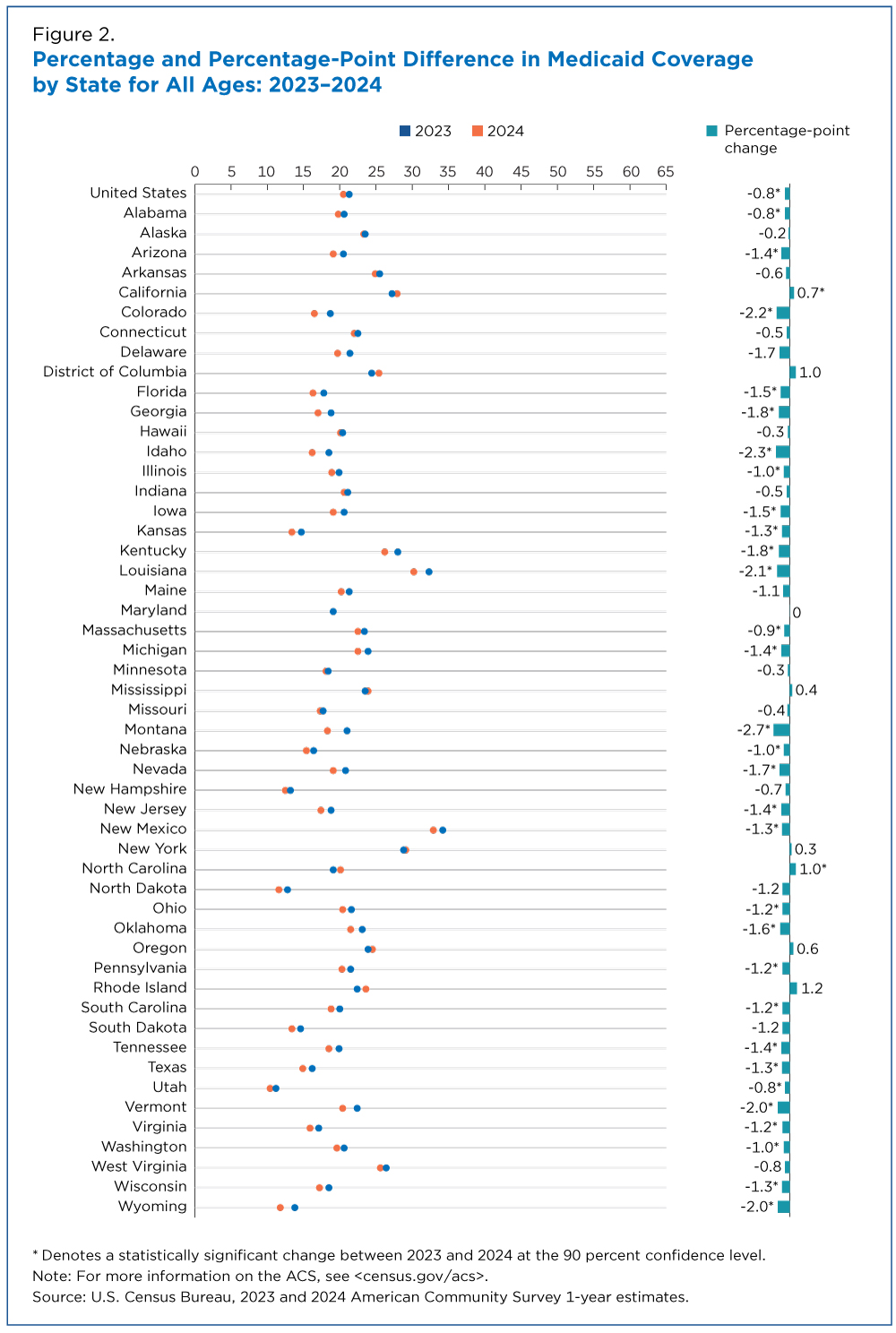
Children experienced the steepest reductions in Medicaid.
Between 2023 and 2024, Medicaid declined by 1.5 percentage points among children compared with a 0.8 percentage point drop among those ages 19 to 64.
Idaho, Montana and Wyoming were among the states with the biggest drops in Medicaid coverage of children (Figure 3).
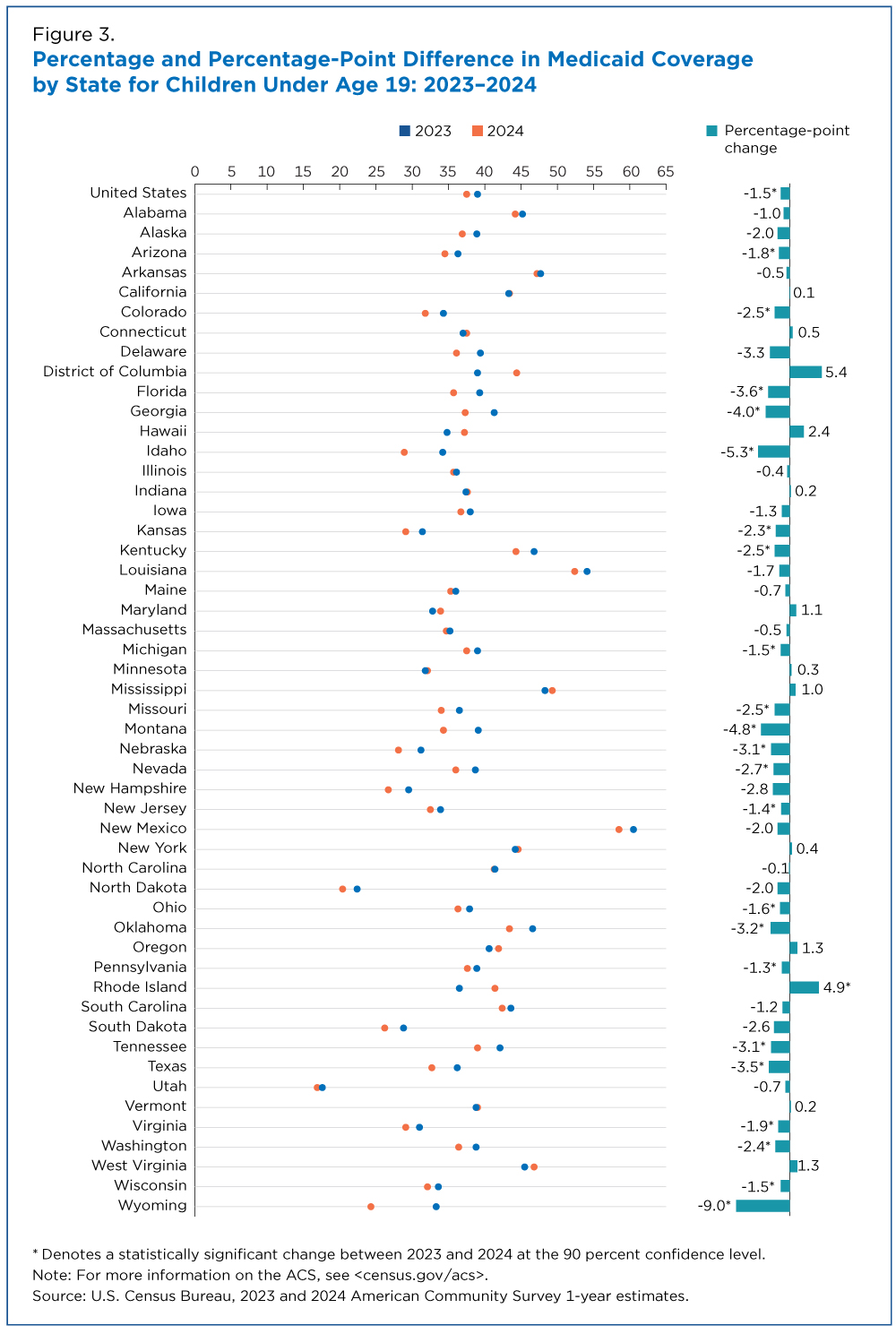
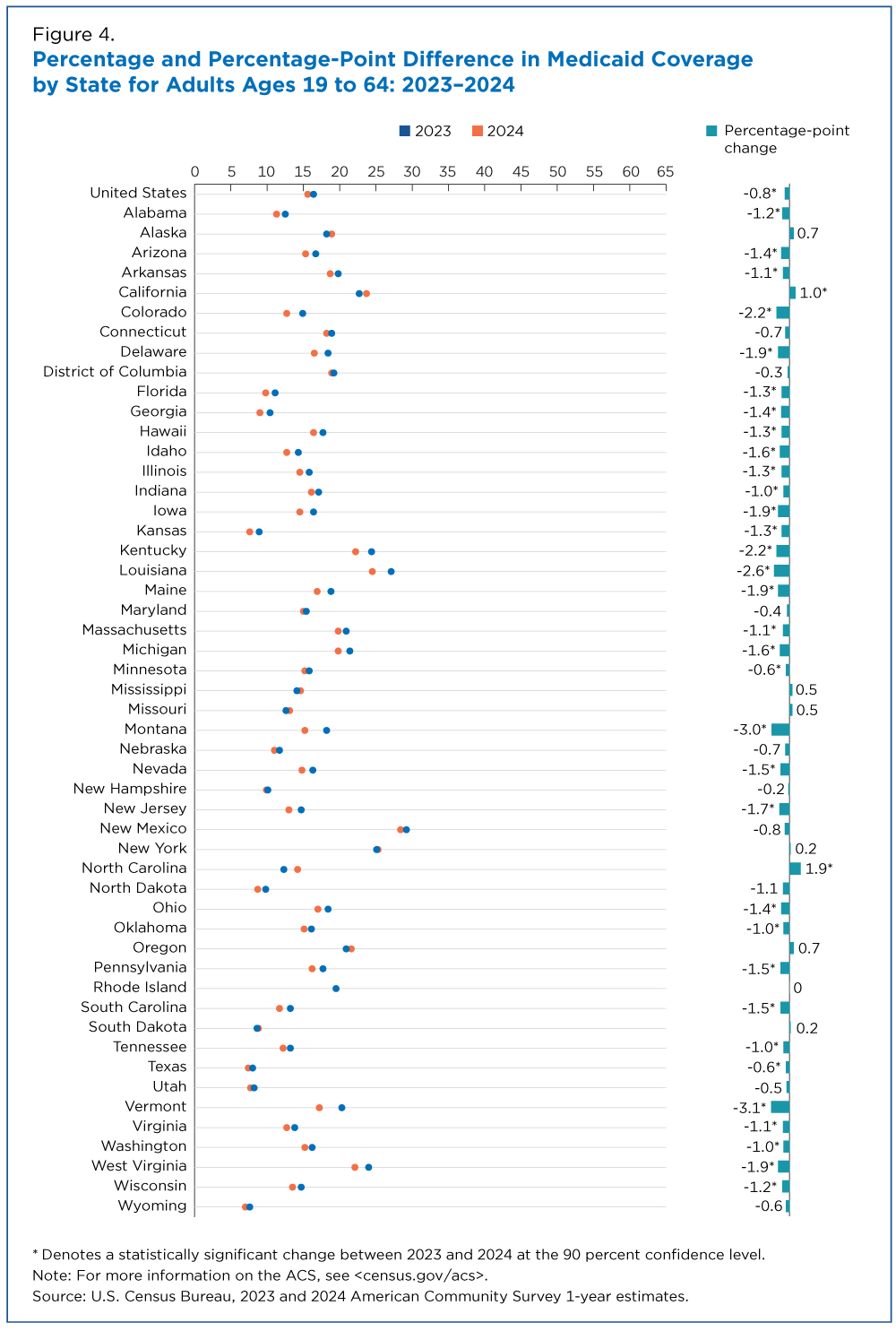
Louisiana, Montana and Vermont had among the largest declines in Medicaid coverage of adults ages 19 to 64 (Figure 4).
Related Statistics
Subscribe
Our email newsletter is sent out on the day we publish a story. Get an alert directly in your inbox to read, share and blog about our newest stories.
Contact our Public Information Office for media inquiries or interviews.
-
HousingRecent Homebuyers Face Highest Mortgage Payments in Nearly Two DecadesSeptember 11, 2025Despite higher median monthly mortgage payments, homeowners who moved in 2024 lived in homes with lower median values than those who moved in 2021.
-
HousingNearly a Quarter of Homeowners Paid Condo or HOA Fees in 2024September 11, 2025New data show that about 5.5 million households paid less than $50 a month and 3 million over $500 in condo or homeowners association fees in 2024.
-
Health InsuranceHealth Insurance Coverage Varied Significantly by OccupationSeptember 09, 2025In 2024, farming, fishing and forestry occupations had among the highest uninsured rates among workers ages 19 to 64.
-
IncomeHow Income Varies by Race and GeographyJanuary 29, 2026Median income of non-Hispanic White households declined in five states over the past 15 years: Alaska, Connecticut, Louisiana, Nevada, and New Mexico.
-
HousingRental Costs Up, Mortgages Stayed FlatJanuary 29, 2026Newly Released American Community Survey compares 2020-2024 and 2015-2019 housing costs by county.
-
HousingShare of Owner-Occupied, Mortgage-Free Homes Up in 2024January 29, 2026The share of U.S. homeowners without a mortgage was higher in 2024 than a decade earlier nationwide and in every state, though not all counties saw increases.
-
PopulationU.S. Population Growth Slowest Since COVID-19 PandemicJanuary 27, 2026The decline in international migration was felt across the states, though its impact varied.